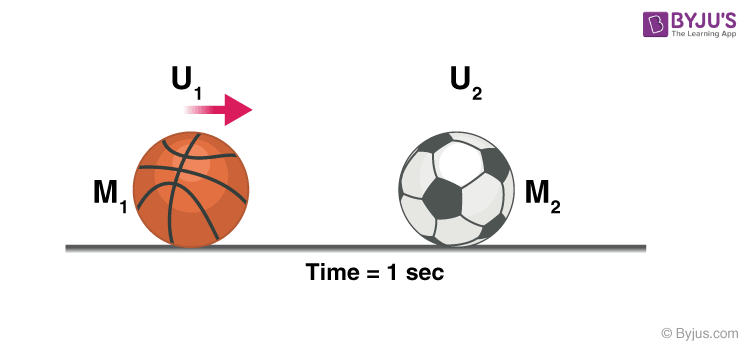
Momentum Definition Science
The amount of momentum that an object has is dependent upon two variables. Momentum is a vector quantity.
What Are Momentum And Impulse Article Khan Academy
Impulse has the same units as momentum kgms or Ns.
Momentum definition science. Momentum is the product of mass and velocity. In physics the formula is momentum mass x velocity. In physics momentum of an object is equal to the mass times the velocity.
Momentum is inertia in motion and defined as an objects mass times velocity. Momentum synonyms momentum pronunciation momentum translation English dictionary definition of momentum. Momentum is a measurement of mass in motion.
Momentum is also a business force and can be described as a series of successes. How much stuff is moving and how fast the stuff is moving. Any object that is moving has momentum.
The direction of the momentum of a single object indicates the direction of its motion. It has both magnitude and direction. Below the basic properties of momentum are described in one dimension.
A falling object gains momentum as it falls. Momentum is a vector quantity. But there are other ways to think about momentum.
Ie it has both magnitude and direction. The American Heritage Student Science. For example an elephant has no momentum when it.
Momentum is the product of mass and velocity. A property of a moving body that determines the length of time required to bring it to rest when under the action of a constant force or moment. Physical Science - Momentum.
How to use momentum in a sentence. And the change in momentum ΔP is also equal to the impulse J. For example an elephant has no momentum when.
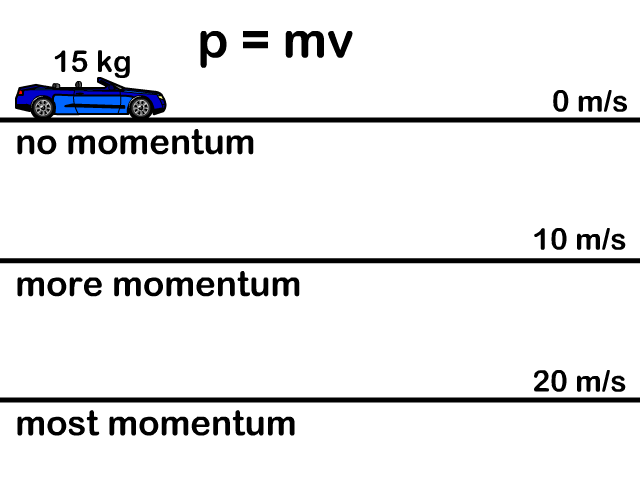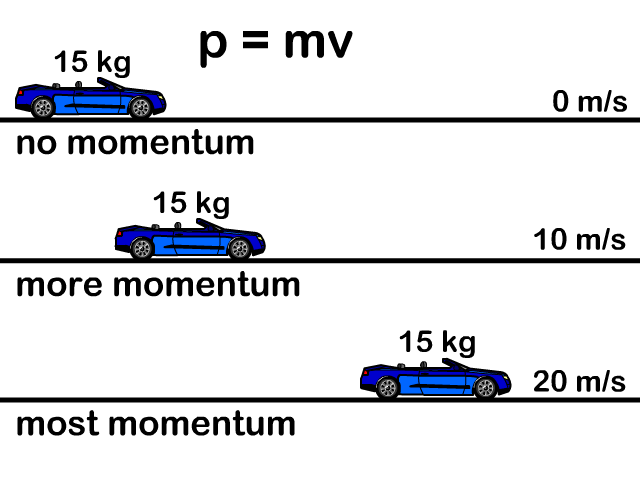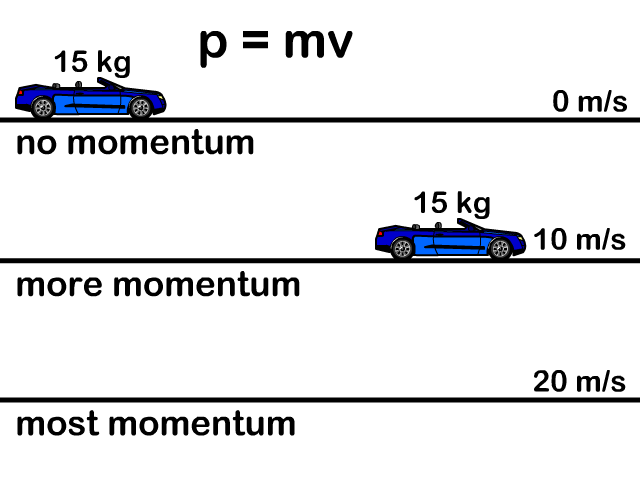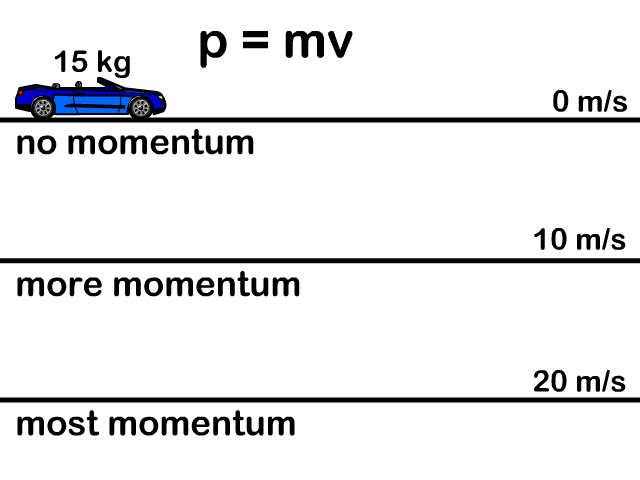
This simple relationship means that doubling either the mass or velocity of an object will simply double the momentum. Scientific definitions for momentum momentum mō-mĕn təm Plural momenta momentums A vector quantity that expresses the relation of the velocity of a body wave field or other physical system to its energy. Momentum In physics momentum is the product of the mass and velocity of an object.
It is usually given the symbol. Measure of how difficult it is to stop an object. Momentum can be measured and is usually done as kilograms x meters per second kgms.
Since momentum has a direction it can be used to predict the resulting direction and speed of motion of objects after they collide. Momentum has the special property that in a closed system it is. Momentum definition physical science.
Momentum definition is - a property of a moving body that the body has by virtue of its mass and motion and that is equal to the product of the bodys mass and velocity. Momentum is also a vector quantity this means it has both a magnitude and an associated direction. A rough scientific definition of momentum is a mass in motion a force.
Momentum is a physical quantity which is closely related to forces. Now up your study game with Learn mode. They are also measured in newton-seconds ns named after the famous scientist Isaac Newton.
In physics momentum is a quantity that can be calculated by multiplying the. The theory of Special Relativity uses the concept of relativistic mass. Momentum product of the mass of a particle and its velocity.
So if an object is moving then it has momentum - it has its mass in motion. Momentum noun U us moʊˈmentəm physics the force or speed of an object in motion or the increase in the rate of development of a process. Symbol p Physics A quantity used to measure the motion of a body.
Momentum is a measurement of mass in motion. In classical mechanics momentum is. Momenta or momentums 1.
Momentum is defined as the quantity of motion of the body. Momentum mass velocity Momentum is usually abbreviated using. How much mass is in how much motion.
How do you calculate momentum. Force F is equal to the change in momentum ΔP over the change in time Δt. Momentum is also a vector quantity this means it has both a magnitude and an associated direction.
By definition Where is the mass and is the velocity. You just studied 25 terms. What is momentum in science definition.
Momentum Mass X Velocity p mv. The standard units for momentum are and momentum is always a vector quantity. Isaac Newtons second law of motion states that the time rate of change of momentum.
Momentum P is equal to mass M times velocity v. It is measured by massvelocity m a s s v e l o c i t y as momentum depends upon velocity and it depends on the direction of the motion of the body as well. Momentum can be defined as mass in motion All objects have mass.
Momentum is a conserved quantity it remains constant unless acted upon by an outside force and is related by Noethers theorem to translational invariance. The word momentum is actually expressed using the letter p so the formula is p m v. Momentum depends upon the variables mass and velocity.
Momentum is a vector quantity since velocity is vector while mass is scalar.
Physics4kids Com Motion Momentum
Momentum Definition Zona Land Education
Physics4kids Com Motion Momentum
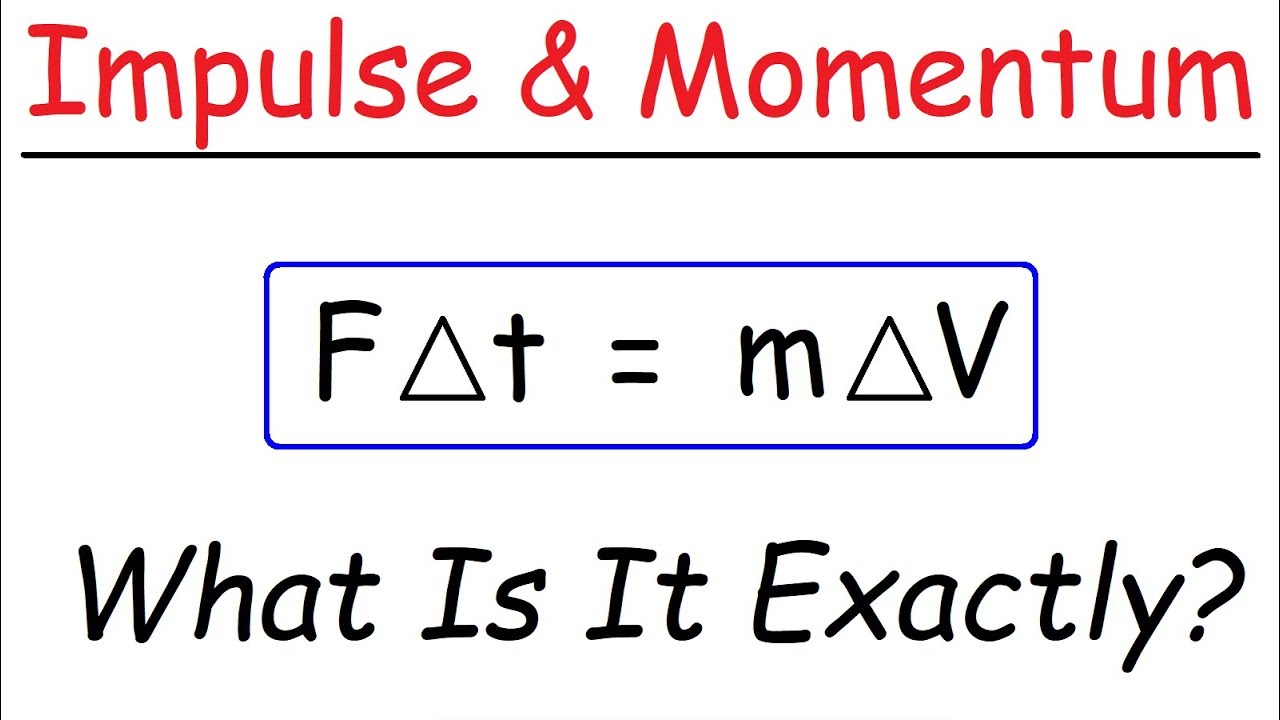
Introduction To Impulse Momentum Physics Youtube
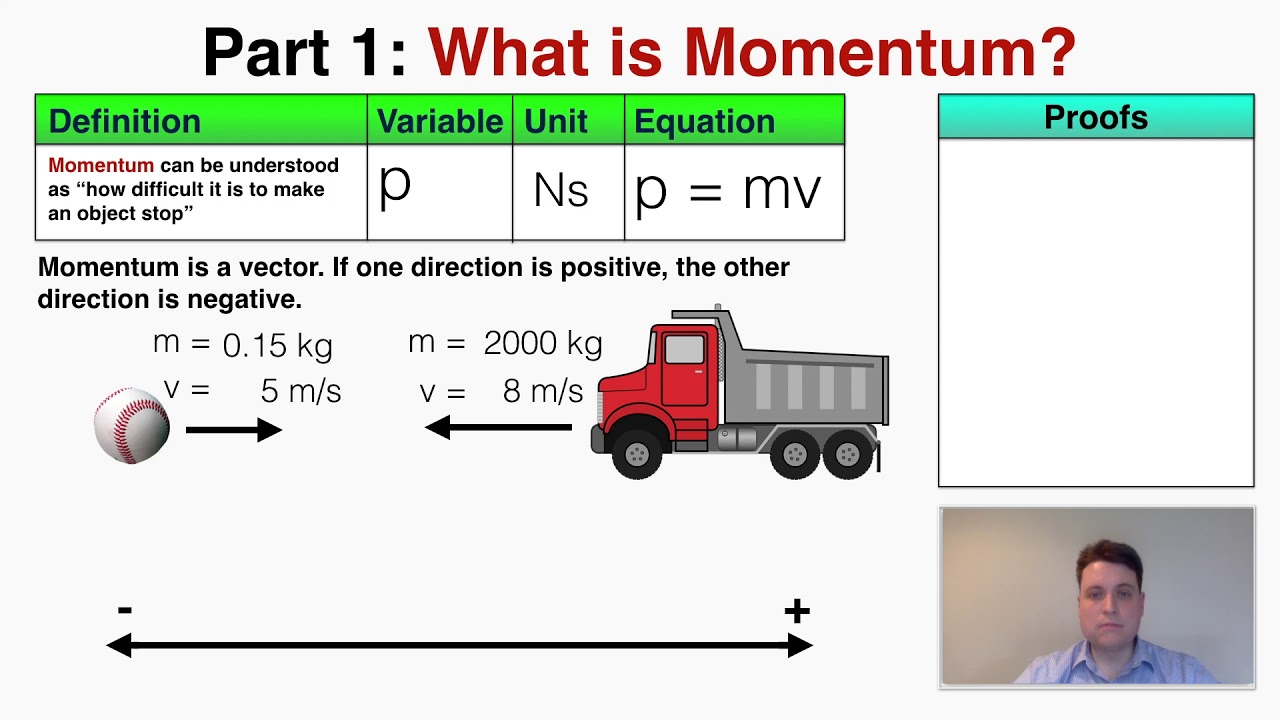
What Is Momentum Ib Physics Youtube

Momentum Concept How It Works And Examples Of Everyday Life
Difference Between Momentum And Impulse Difference Between
Momentum And Impulse Stickman Physics

Momentum Definition Formula Science Notes By Teachoo
Momentum Definition Zona Land Education

Example The Impulse Momentum Theorem Nexus Wiki

Momentum Definition Formula Science Notes By Teachoo

Momentum Formula Definition Equation And Examples
What Is Momentum Physics Youtube
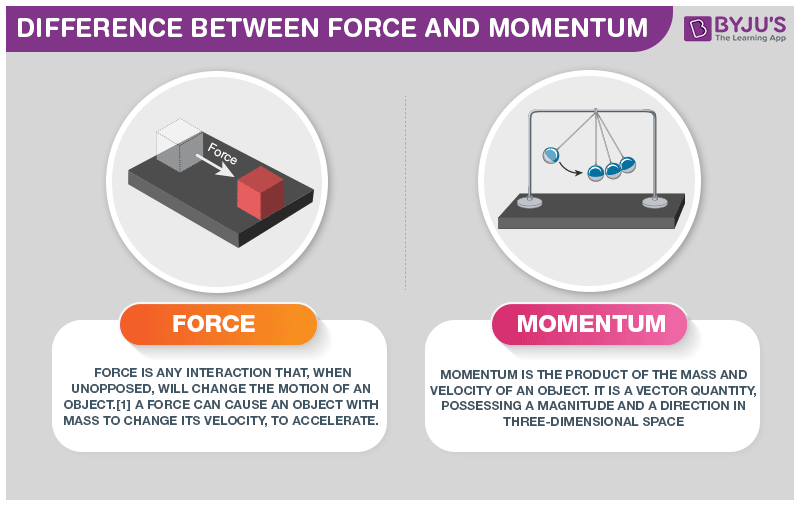
Difference Between Force And Momentum With Its Practical Applications In Real Life
Physics4kids Com Motion Momentum